What is Potassium Carbonate Food Grade?
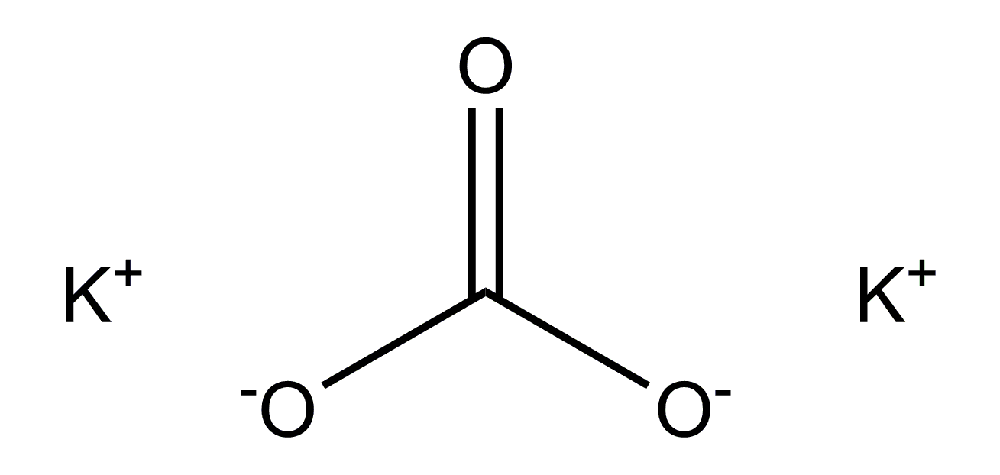
Potassium carbonate (K2CO3) is a white salt, which is soluble in water (insoluble in ethanol) and forms a highly alkaline solution. It can be made as the product of potassium hydroxide’s absorbent reaction with carbon dioxide. It is deliquescent, frequently appearing a moist or damp solid. Potassium carbonate is used in the production of soap and glass.
The History of Potassium Carbonate Food Grade
Potassium carbonate is the primary component of potash and the more refined pearl ash or salts of tartar. Historically, pearl ash was produced by baking potash in a kiln to remove pollutants. The fine, white powder staying was the pearl ash. The very first patent issued by the United States Patent Office was granted to Samuel Hopkins in 1790 for an enhanced method of making potash and pearl ash. In late 18th century The United States and Canada, before the advancement of baking powder, pearl ash was utilized as a leavening agent in quick breads.
How is Potassium Carbonate Food Grade Produced?
Today, potassium carbonate is prepared commercially by the electrolysis of potassium chloride. The resulting potassium hydroxide is then carbonated using carbon dioxide to form potassium carbonate, which is typically utilized to produce other Potassium substances.
2KOH + CO2 → K2CO3 + H2O
Typical Applications for Potassium Carbonate Food Grade
Potassium carbonate has historically been utilized for glass and soap production. Contemporary applications depend on the compound’s fundamental properties, such as its ability to release heat (exothermic), makings it helpful as a deicer. Its water-absorbing properties discover applications in the agrochemical industry and in health and beauty products Additionally, K2CO3 is used to lower the level of acidity of wine and serves as a drying agent for fruit processing, in addition to in formulations for inks and toners, disinfectants and cleaning products.
- For soap, glass, and china production.
- As a moderate drying agent where other drying representatives, such as calcium chloride and magnesium sulfate, might be incompatible. It is not appropriate for acidic substances, however, can be useful for drying an organic stage if one has a percentage of acidic pollutant. It might also be used to dry some ketones, alcohols, and amines before distillation. [4] in food, where it has lots of standard uses. It is an ingredient in the production of yard jelly, food consumed
in Chinese and Southeast Asian cuisines, as well as Chinese noodles and mooncake. It is utilized to tenderize tripe. German gingerbread dishes often use potassium carbonate as a baking agent, although in combination with hartshorn. It is however essential that the right quantities are utilized to prevent harm, and cooks ought to not use it without guidance. - In the production of cocoa powder to balance the pH (i.e., minimize the level of acidity) of natural cocoa beans; it also improves aroma. The process of adding potassium carbonate to cocoa powder is generally called “Dutching” (and the products referred to as Dutch-processed cocoa powder), as the process was very first developed in 1828 by Coenraad Johannes van Houten, a Dutchman.
- As a buffering agent in the production of mead or wine.
- In ancient documents, it is reported to have been utilized to soften hard water. [5] as a fire suppressant in snuffing out deep-fat fryers and different other B class-related fires.
- In condensed aerosol fire suppression, although as the byproduct of potassium nitrate.
- As an ingredient in welding fluxes, and in the flux covering on arc-welding rods.
- As an animal feed ingredient to please the potassium requirements of farmed animals such as broiler breeders
How does Potassium Carbonate Food Grade look and how can it be utilized?
White crystal granule, As a leavening agent for drinks, A moderate preservative and to Add potassium
Is potassium carbonate as a food additive safe for health?
Potassium carbonate is produced synthetically for business use by the electrolysis of potassium chloride, which is a natural mineral. Potassium carbonate has been used for ages for example to make soap. It is utilized as a level of acidity regulator, and buffering agent in lots of foods like in bakeshop items, soft drinks, cocoa, confectionery, custard powder, mead, and wine.
It is EU authorized additive, and the E-number is: E501 and is also a subject to specific quantitative limits. It is also approved in the U.S.A. and Australia & New Zealand.
There is no sign that this chemical might be carcinogenic or mutagenic, but it can be toxic if in contact with skin and eyes, swallowed or breathed in.
In supplements: because potassium supplements can cause high potassium levels, which is more unsafe than low potassium, do not take potassium bicarbonate without very first consulting your health care provider.
Here you can learn how and where you can use this additive in the EU: FOODS SYSTEM. It also can be utilized by all religious groups, vegans and vegetarians, it is not from animal origin.
There are no known negative results at this minute noted. According to the FDA, PB is usually acknowledged as safe (GRAS). However, some individuals experience the following adverse effects: abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, vomiting, or nausea.
Other terms for potassium carbonate (these also may be used for non-food grade products):.
- Carbonate of potash.
- Dipotassium carbonate.
- Dipotassium salt.
- Pearl-ash.
- Potash.
- Salt of tartar.
- Salt of wormwood.


Leave a Reply